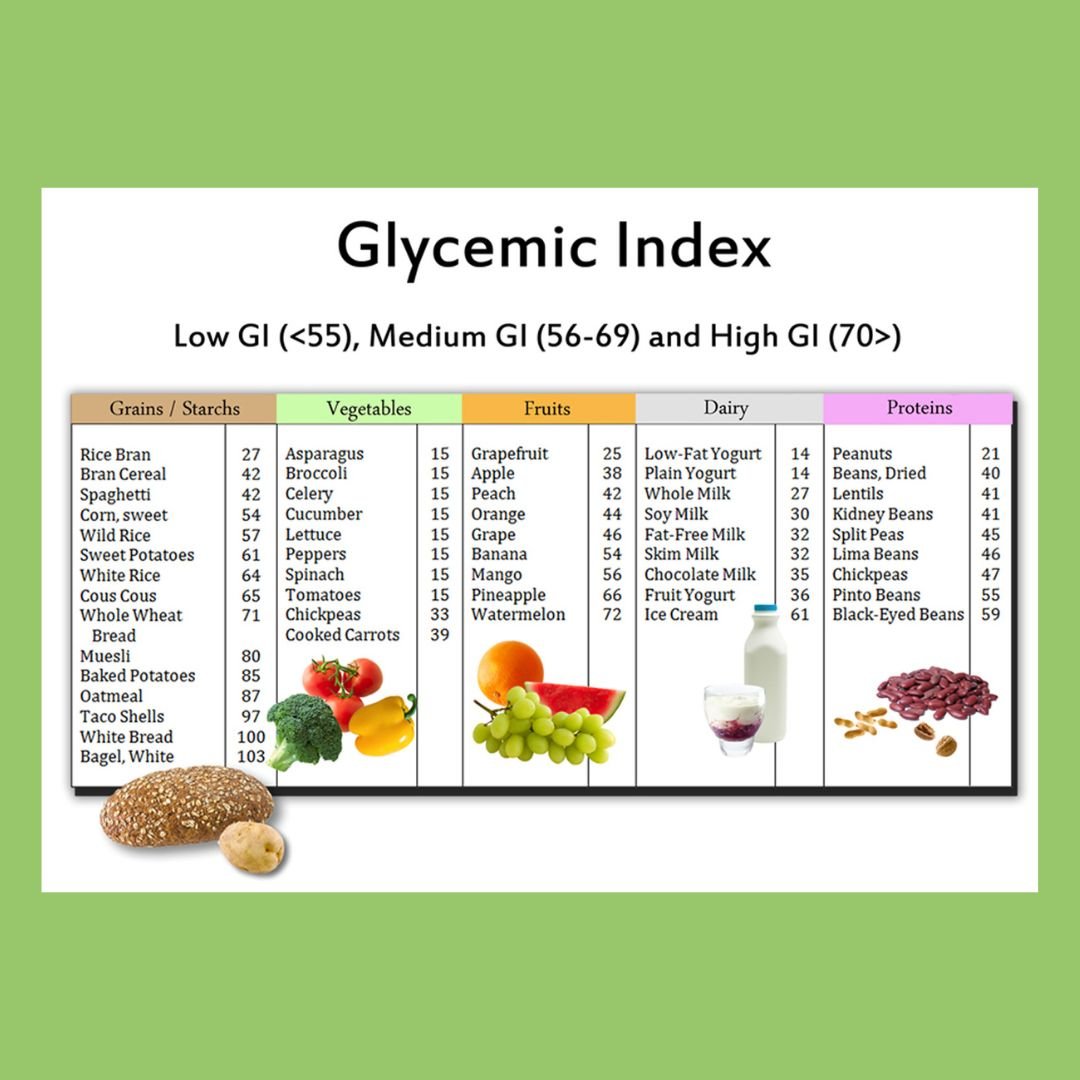
Here's a simple explanation of what low GI foods are and why they are better for you when managing a low carb diet.
Low glycemic foods are foods that have a lower impact on blood sugar levels when consumed compared to high glycemic foods. The glycemic index (GI) is a ranking system that measures how quickly carbohydrates in foods raise blood sugar levels. Foods with a low glycemic index are digested and absorbed more slowly, leading to a slower and more gradual increase in blood sugar levels.
Low glycemic foods are often recommended for individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels more effectively. They can also be beneficial for promoting sustained energy levels and overall health. Here's a breakdown of low glycemic foods and their benefits:
Examples of Low Glycemic Foods:
- Non-starchy vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, peppers, zucchini, tomatoes.
- Whole grains: Whole oats, quinoa, barley, whole wheat, whole grain pasta.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, kidney beans.
- Fruits: Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries), apples, pears, oranges, peaches.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds.
- Dairy: Greek yogurt, plain yogurt.
- Protein sources: Lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs.
Benefits of Low Glycemic Foods:
-
Stabilized Blood Sugar Levels: Low glycemic foods help prevent rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels, providing more stable energy throughout the day.
-
Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Consistently consuming low glycemic foods may help improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to use insulin effectively.
-
Weight Management: Low glycemic foods can contribute to feelings of fullness and satiety, which may help with weight management and reducing overeating.
-
Longer Sustained Energy: Foods with a lower glycemic index provide a steady source of energy, helping to avoid energy crashes after meals.
-
Heart Health: Many low glycemic foods, such as whole grains, legumes, and fruits, are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals that support heart health.
-
Reduced Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A diet rich in low glycemic foods may help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, especially in individuals at risk.
It's important to note that the glycemic index is not the only factor to consider when making dietary choices. Portion size, nutrient content, and how foods are prepared can also impact their effect on blood sugar levels. Additionally, a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods is important for overall health.
If you have diabetes or are looking to manage your blood sugar levels, working with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can help you create a personalized meal plan that includes appropriate low glycemic foods while considering your individual dietary preferences and health goals.