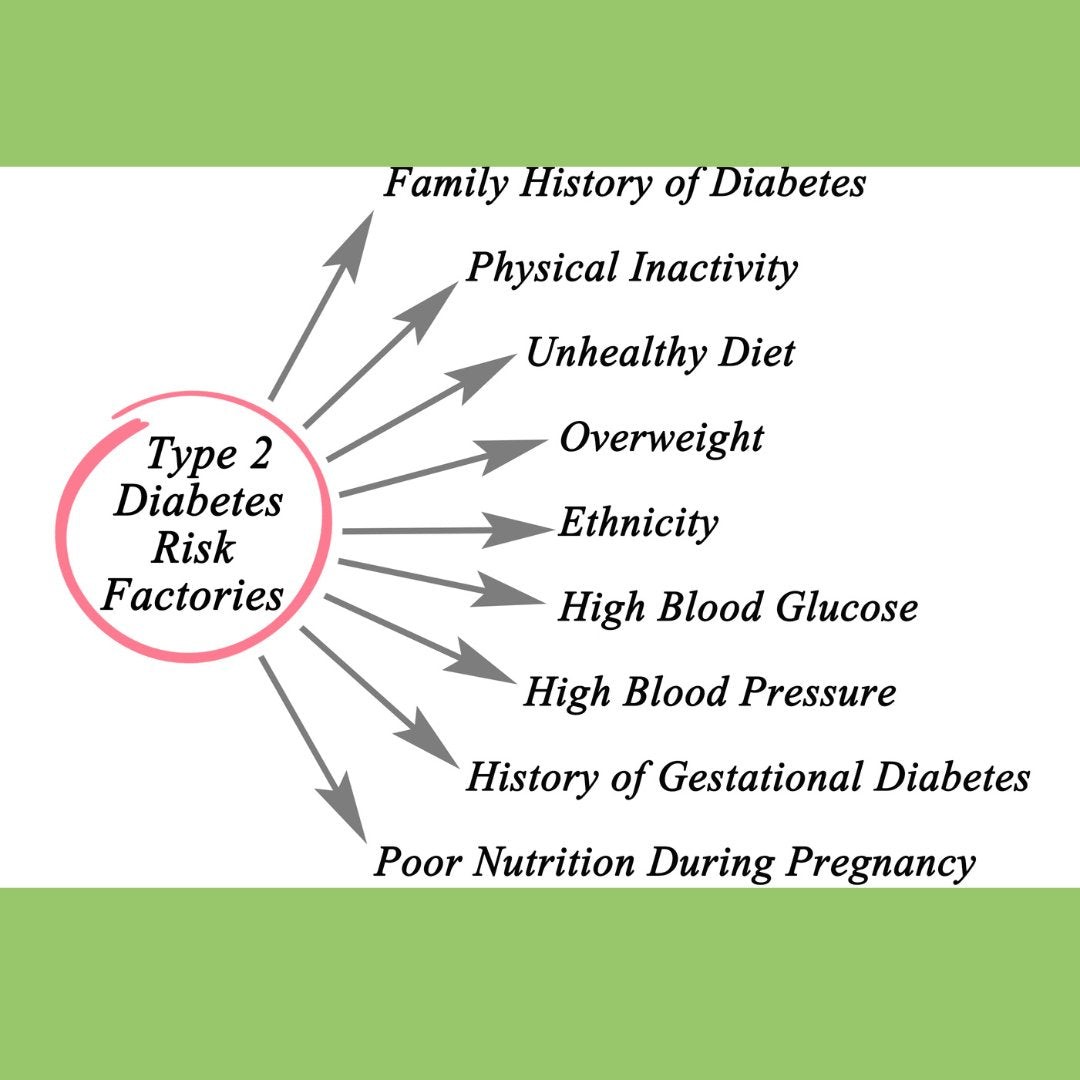
High blood sugar levels are the result of type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion. Although type 2 diabetes is generally regarded as a progressive condition necessitating perpetual care, it is occasionally reversible or effectively manageable with the implementation of medical interventions, weight loss programs, and lifestyle modifications.
Reversal of type 2 diabetes pertains to the attainment and maintenance of normalized blood glucose levels, eliminating the necessity for insulin therapy or diabetes medications. Although complete reversal of type 2 diabetes may not be possible for all individuals, substantial enhancements in blood sugar regulation and general well-being can be attained by many through the adoption of healthy lifestyle practices.
The following strategies may be effective in reversing or ameliorating type 2 diabetes:
Weight Loss: Individuals with type 2 diabetes may experience improved insulin sensitivity and blood sugar regulation through the loss of excess body weight, particularly abdominal obesity. Notably enhanced glycemic control can result from even modest weight reductions of 5-10% of body weight.
A nutritious and well-balanced diet can aid in the regulation of blood sugar levels and facilitate weight loss. Incorporate a variety of nutritious fats, fruits, vegetables, whole cereals, and lean proteins into your diet, while limiting your intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-fat foods.
Consistent physical activity, including but not limited to vigorous walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming, has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity, reduce blood glucose levels, and facilitate weight loss. Aim to complete at least 150 minutes of aerobic exercise per week at a moderate intensity, in addition to at least two days per week of muscle-strengthening activities.
Medications: Metformin and other oral diabetes medications may be prescribed in certain instances to assist in reducing blood sugar levels and enhancing insulin sensitivity. In conjunction with modifications to one's lifestyle, these medications are frequently employed to attain ideal glycemic control.
Bariatric surgery, including sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass, may be an option to consider for patients who are uncontrolled type 2 diabetes and severely obese. In numerous instances, bariatric surgery can result in substantial weight reduction and amelioration or resolution of type 2 diabetes.
Although some individuals have the potential to reverse type 2 diabetes, it is critical to acknowledge that sustaining the progress necessitates a continuous dedication to healthy lifestyle choices, consistent adherence to treatment guidelines, and regular medical monitoring. Furthermore, it is important to note that complete reversal of type 2 diabetes is not a realistic expectation for all individuals, and the efficacy of interventions can differ based on personal characteristics including age, diabetes duration, and the presence of complications. Individuals with type 2 diabetes must therefore collaborate closely with their healthcare providers to develop an individualized treatment plan that meets their specific requirements and objectives.
Reversal of type 2 diabetes pertains to the attainment and maintenance of normalized blood glucose levels, eliminating the necessity for insulin therapy or diabetes medications. Although complete reversal of type 2 diabetes may not be possible for all individuals, substantial enhancements in blood sugar regulation and general well-being can be attained by many through the adoption of healthy lifestyle practices.
The following strategies may be effective in reversing or ameliorating type 2 diabetes:
Weight Loss: Individuals with type 2 diabetes may experience improved insulin sensitivity and blood sugar regulation through the loss of excess body weight, particularly abdominal obesity. Notably enhanced glycemic control can result from even modest weight reductions of 5-10% of body weight.
A nutritious and well-balanced diet can aid in the regulation of blood sugar levels and facilitate weight loss. Incorporate a variety of nutritious fats, fruits, vegetables, whole cereals, and lean proteins into your diet, while limiting your intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-fat foods.
Consistent physical activity, including but not limited to vigorous walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming, has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity, reduce blood glucose levels, and facilitate weight loss. Aim to complete at least 150 minutes of aerobic exercise per week at a moderate intensity, in addition to at least two days per week of muscle-strengthening activities.
Medications: Metformin and other oral diabetes medications may be prescribed in certain instances to assist in reducing blood sugar levels and enhancing insulin sensitivity. In conjunction with modifications to one's lifestyle, these medications are frequently employed to attain ideal glycemic control.
Bariatric surgery, including sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass, may be an option to consider for patients who are uncontrolled type 2 diabetes and severely obese. In numerous instances, bariatric surgery can result in substantial weight reduction and amelioration or resolution of type 2 diabetes.
Although some individuals have the potential to reverse type 2 diabetes, it is critical to acknowledge that sustaining the progress necessitates a continuous dedication to healthy lifestyle choices, consistent adherence to treatment guidelines, and regular medical monitoring. Furthermore, it is important to note that complete reversal of type 2 diabetes is not a realistic expectation for all individuals, and the efficacy of interventions can differ based on personal characteristics including age, diabetes duration, and the presence of complications. Individuals with type 2 diabetes must therefore collaborate closely with their healthcare providers to develop an individualized treatment plan that meets their specific requirements and objectives.